Streaming the Camera Image
Introduction
The camera image streaming implementation on the Vision-RTK 2 employs the Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP), which is a well-established network protocol for delivering video over IP networks. It runs over the User Datagram Protocol (UDP). RTP is designed for end-to-end, real-time transfer of streaming media. The protocol provides facilities for jitter compensation and detection of packet loss and out-of-order delivery, which are common, especially during UDP transmissions on an IP network. RTP allows data transfer to multiple destinations through IP multicast.
Camera image stream using the Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) is available since FW2.85.x.
Some notes and warnings:
For the best performance, the images should always be streamed via Ethernet. Image interference commonly occurs during transmission over WLAN.
The streamed images are compressed to reduce CPU load.
The receiver must be capable of RTP as well as understand the selected encoding.
The camera's intrinsic data is available to users upon request. The reference camera model is based on the OpenCV Fish-eye Camera Calibration documentation: https://docs.opencv.org/3.4/db/d58/group__calib3d__fisheye.html#details.
Usage
VRTK2
The camera stream is not enabled by default. To enable it, head to the "Configuration → Camera" page and change the "Enable stream" status.
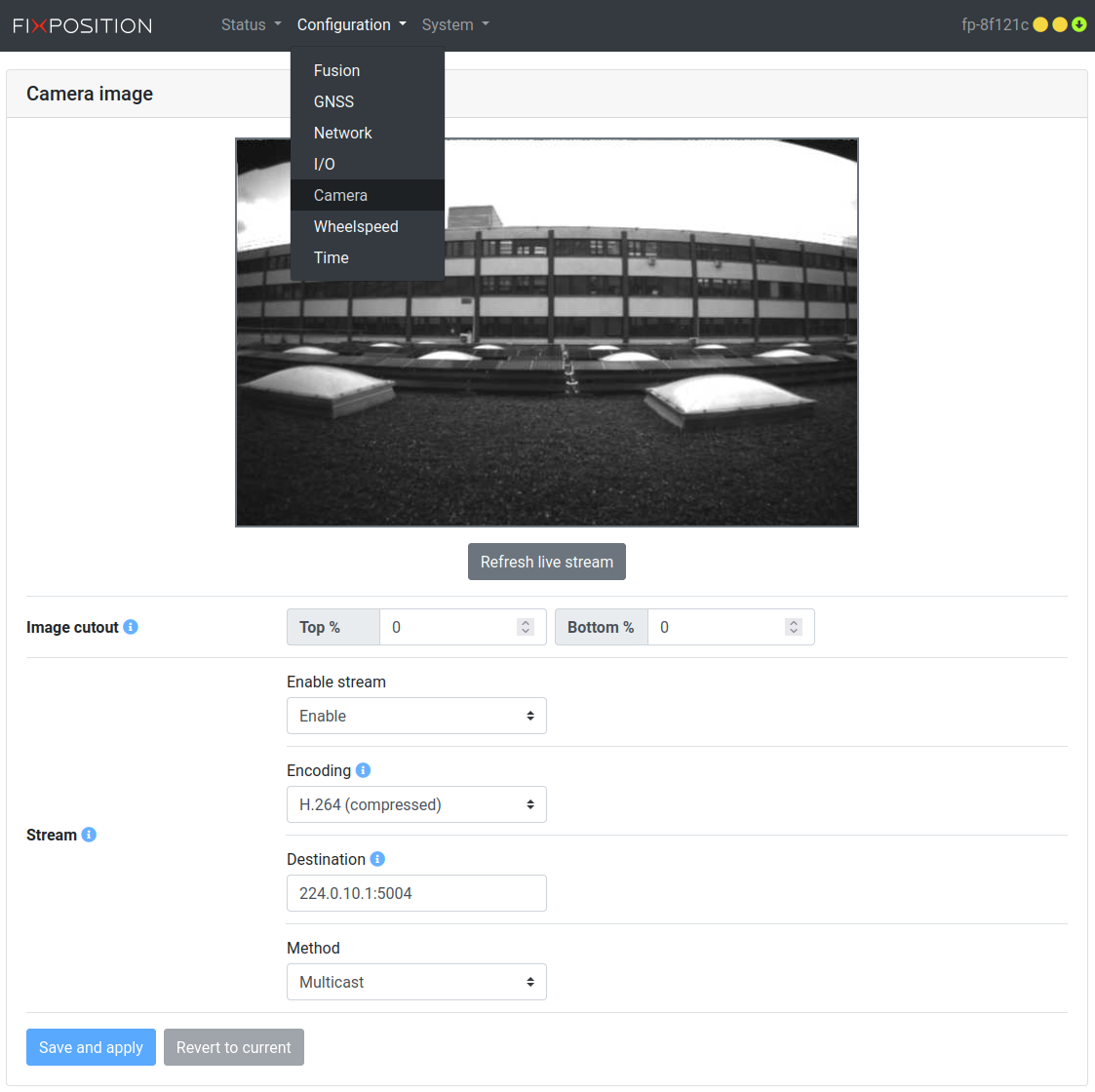
Camera stream configuration
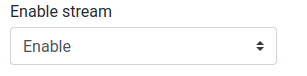
Enable stream option
Two different encodings can be selected in the Encoding setting: H264 or H265.
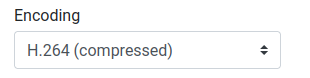
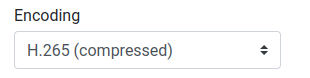
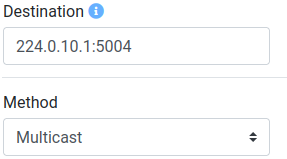
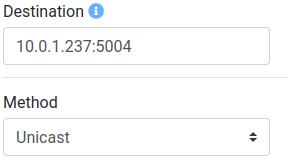
Depending on the streaming method used, different UDP destinations can be chosen:
Multicast (Please refer to https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Multicast_address for a list of allowed multicast addresses)
Unicast
RAW streaming
High Load!: The streaming of RAW images affects the sensor performance during use, as a higher system load is generated.
On the sensor in the ‘System → Tool’ page set the
camstrraw=1Advance option.

On the sensor in the ‘Configuration → Camera’ page select “Raw (uncompressed)”.

Client
The receiver must be capable of RTP as well as understand the selected encoding. Below are a few examples of how the camera image can be streamed over RTP/UDP.
For demonstration purposes, streaming via WLAN is also possible, but unicast must be used and the destination IP (e.g., from the laptop) must be properly configured both in the web interface and in the unicast-h264/5.sdp file.
1. Linux
Multicast:
H264 Encoding (adapt IP/port if needed)
Play
CODEgst-launch-1.0 udpsrc multicast-group=224.0.10.1 auto-multicast=true port=5004 caps = "application/x-rtp, media=(string)video, clock-rate=(int)90000, encoding-name=(string)H264, payload=(int)96" ! rtph264depay ! decodebin ! autovideosink sync=falseRecord (.mkv)
CODEgst-launch-1.0 udpsrc multicast-group=224.0.10.1 auto-multicast=true port=5004 caps = "application/x-rtp, media=(string)video, clock-rate=(int)90000, encoding-name=(string)H264, payload=(int)96" ! rtph264depay ! h264parse ! matroskamux ! filesink location=~/camera.mkvRecord (.mpeg)
CODEgst-launch-1.0 udpsrc multicast-group=224.0.10.1 auto-multicast=true port=5004 caps = "application/x-rtp, media=(string)video, clock-rate=(int)90000, encoding-name=(string)H264, payload=(int)96" ! rtph264depay ! h264parse ! mpegtsmux ! filesink location=~/camera.mpeg
H265 Encoding (adapt IP/port if needed)
Play
CODEgst-launch-1.0 udpsrc multicast-group=224.0.10.1 auto-multicast=true port=5004 caps = "application/x-rtp, media=(string)video, clock-rate=(int)90000, encoding-name=(string)H265, payload=(int)96" ! rtph265depay ! decodebin ! autovideosink sync=falseRecord (.mkv)
CODEgst-launch-1.0 udpsrc multicast-group=224.0.10.1 auto-multicast=true port=5004 caps = "application/x-rtp, media=(string)video, clock-rate=(int)90000, encoding-name=(string)H265, payload=(int)96" ! rtph265depay ! h265parse ! matroskamux ! filesink location=~/camera.mkvRecord (.mpeg)
CODEgst-launch-1.0 udpsrc multicast-group=224.0.10.1 auto-multicast=true port=5004 caps = "application/x-rtp, media=(string)video, clock-rate=(int)90000, encoding-name=(string)H265, payload=(int)96" ! rtph265depay ! h265parse ! mpegtsmux ! filesink location=~/camera.mpeg
RAW (unencoded) (adapt IP/port if needed)
Play
CODEgst-launch-1.0 udpsrc multicast-group=224.0.10.1 auto-multicast=true port=5004 caps="application/x-rtp, media=(string)video, clock-rate=(int)90000, encoding-name=(string)RAW, sampling=(string)YCbCr-4:2:0, depth=(string)8, width=(string)640, height=(string)400, payload=(int)96" ! rtpvrawdepay ! decodebin ! autovideosink sync=falseRecord (.raw)
CODEgst-launch-1.0 udpsrc multicast-group=224.0.10.1 auto-multicast=true port=5004 caps="application/x-rtp, media=(string)video, clock-rate=(int)90000, encoding-name=(string)RAW, sampling=(string)YCbCr-4:2:0, depth=(string)8, width=(string)640, height=(string)400, payload=(int)96" ! rtpvrawdepay ! filesink location=~/camera.raw
Unicast:
H264 Encoding (adapt port if needed)
Play
CODEgst-launch-1.0 udpsrc port=5004 caps = "application/x-rtp, media=(string)video, clock-rate=(int)90000, encoding-name=(string)H264, payload=(int)96" ! rtph264depay ! decodebin ! autovideosink sync=falseRecord (.mkv)
CODEgst-launch-1.0 udpsrc port=5004 caps = "application/x-rtp, media=(string)video, clock-rate=(int)90000, encoding-name=(string)H264, payload=(int)96" ! rtph264depay ! h264parse ! matroskamux ! filesink location=~/camera.mkvRecord (.mpeg)
CODEgst-launch-1.0 udpsrc port=5004 caps = "application/x-rtp, media=(string)video, clock-rate=(int)90000, encoding-name=(string)H264, payload=(int)96" ! rtph264depay ! h264parse ! mpegtsmux ! filesink location=~/camera.mpeg
H265 Encoding (adapt port if needed)
Play
CODEgst-launch-1.0 udpsrc port=5004 caps = "application/x-rtp, media=(string)video, clock-rate=(int)90000, encoding-name=(string)H265, payload=(int)96" ! rtph265depay ! decodebin ! autovideosink sync=falseRecord (.mkv)
CODEgst-launch-1.0 udpsrc port=5004 caps = "application/x-rtp, media=(string)video, clock-rate=(int)90000, encoding-name=(string)H265, payload=(int)96" ! rtph265depay ! h265parse ! matroskamux ! filesink location=~/camera.mkvRecord (.mpeg)
CODEgst-launch-1.0 udpsrc port=5004 caps = "application/x-rtp, media=(string)video, clock-rate=(int)90000, encoding-name=(string)H265, payload=(int)96" ! rtph265depay ! h265parse ! mpegtsmux ! filesink location=~/camera.mpeg
RAW (unencoded) (adapt port if needed)
Play
CODEgst-launch-1.0 udpsrc auto-multicast=true port=5004 caps="application/x-rtp, media=(string)video, clock-rate=(int)90000, encoding-name=(string)RAW, sampling=(string)YCbCr-4:2:0, depth=(string)8, width=(string)640, height=(string)400, payload=(int)96" ! rtpvrawdepay ! decodebin ! autovideosink sync=falseRecord (.raw)
CODEgst-launch-1.0 udpsrc auto-multicast=true port=5004 caps="application/x-rtp, media=(string)video, clock-rate=(int)90000, encoding-name=(string)RAW, sampling=(string)YCbCr-4:2:0, depth=(string)8, width=(string)640, height=(string)400, payload=(int)96" ! rtpvrawdepay ! filesink location=~/camera.raw
Multicast:
H264 Encoding (use multicast-h264.sdp and adapt IP/port if needed)
Play
CODEffplay -protocol_whitelist file,crypto,rtp,udp -fflags nobuffer -flags low_delay -probesize 32 -analyzeduration 1 -strict experimental -framedrop -vf setpts=0 multicast-h264.sdpRecord (.mkv)
CODEffmpeg -protocol_whitelist file,crypto,rtp,udp -fflags nobuffer -flags low_delay -probesize 32 -analyzeduration 1 -strict experimental -i multicast-h264.sdp -c:v vp9 camera.mkv
H265 Encoding (use multicast-h265.sdp and adapt IP/port if needed)
Play
CODEffplay -protocol_whitelist file,crypto,rtp,udp -fflags nobuffer -flags low_delay -probesize 32 -analyzeduration 1 -strict experimental -framedrop -vf setpts=0 multicast-h265.sdpRecord (.mkv)
CODEffmpeg -protocol_whitelist file,crypto,rtp,udp -fflags nobuffer -flags low_delay -probesize 32 -analyzeduration 1 -strict experimental -i multicast-h265.sdp -c:v vp9 camera.mkv
Unicast: The same FFmpeg configuration files can be used for unicast streaming. Simply replace the multicast address with the unicast address.
CODEc=IN IP4 10.0.1.237
multicast-h264.sdp multicast-h265.sdp
2. Windows
FFmpeg can be used on Windows. Unpack the following ZIP file and execute the required script (.bat):
